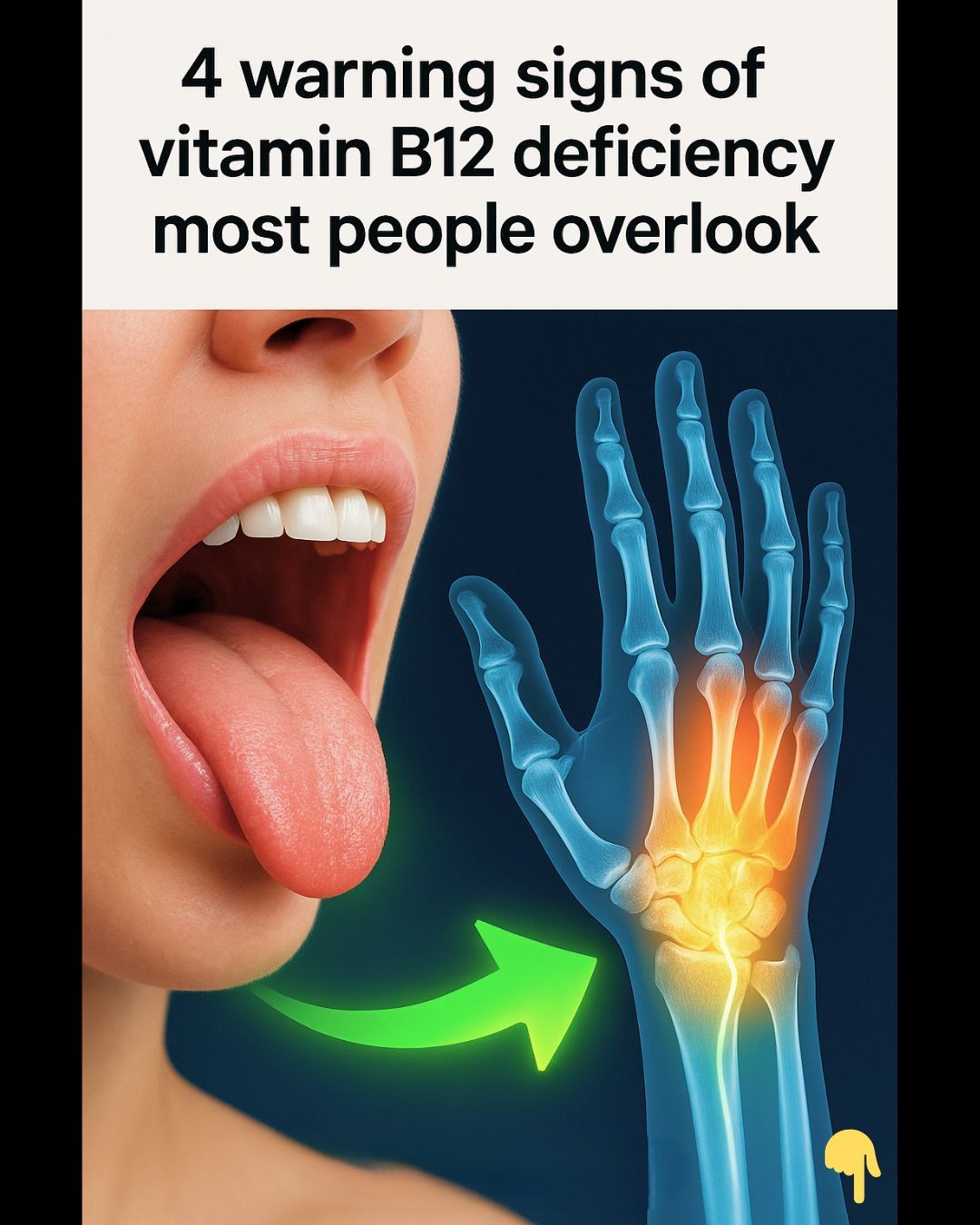
Deficiency can also manifest in the mouth and digestive system:
- Glossitis: A swollen, inflamed tongue that may appear smooth and red.
- Loss of Appetite: A decrease in hunger can lead to weight loss.
- Digestive Issues: Symptoms like diarrhea or constipation may occur.
4. Ocular Symptoms
Vitamin B12 deficiency can affect your vision:
- Vision Changes: Difficulty seeing in low light or changes in color perception.
- Optic Nerve Damage: This can lead to vision loss if not addressed.
Who Is At Risk?
Certain groups are more susceptible to Vitamin B12 deficiency:
- Vegetarians and Vegans: Since B12 is primarily found in animal products, those on plant-based diets need to be cautious.
- Older Adults: Aging can affect the absorption of B12 due to decreased stomach acid production.
- Individuals with Digestive Disorders: Conditions like Crohn’s disease or those who have had gastric surgery may struggle to absorb B12.
How to Increase Vitamin B12 Levels
If you suspect you have a deficiency, here are some ways to boost your levels:
- Dietary Sources: Include more animal products like meat, fish, eggs, and dairy in your diet.
- Fortified Foods: Look for plant-based milks, cereals, and nutritional yeast that are fortified with B12.
- Supplements: Consider taking a B12 supplement, especially if you are at risk. There are two main types:
- Cyanocobalamin: A synthetic form that is converted to active forms in the body.
- Methylcobalamin: An active form that may be more effective for some individuals.
Treatment for Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Continue reading by clicking the ( NEXT 》 ) button below !